Diabetes can be a silent threat, especially in the elderly. Recognizing what are the signs of diabetes in the elderly is crucial for early intervention. Symptoms like increased thirst and frequent urination may seem harmless but can signal serious health issues. Unexplained weight loss and fatigue often lead to confusion about aging versus illness.
Ignoring these signs can result in severe complications. The difference between managing diabetes effectively and facing dire consequences lies in awareness. This guide will help you spot these warning signals early on. Understanding these signs empowers caregivers and families to take proactive steps toward better health outcomes for their loved ones.
Understanding Diabetes in the Elderly
Diabetes Definition
Diabetes is a chronic condition. It affects how the body processes glucose, or sugar. There are two main types: Type 1 and Type 2. Type 2 diabetes is more common among diabetic seniors. This type occurs when the body becomes resistant to insulin. Insulin helps cells absorb glucose for energy.
Prevalence Among Older Adults
Diabetes prevalence increases with age. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), about 25% of adults aged 65 and older have diabetes. This number is expected to rise as the population ages. By 2030, the CDC estimates that over 60 million seniors will be living with diabetes in the United States.
Risk Factors for Seniors
Several risk factors contribute to diabetes in elderly individuals. These include:
Obesity: Excess weight can lead to insulin resistance.
Sedentary Lifestyle: Lack of physical activity increases the risk.
Family History: Genetics play a role in developing diabetes.
Age: Aging itself increases susceptibility to diabetes.
High Blood Pressure: This often coexists with diabetes.
Understanding these factors helps in identifying those at risk.
Effects of Aging on Blood Sugar Management
Aging impacts how the body manages blood sugar levels. As people grow older, their bodies may produce less insulin. Muscle mass decreases, which affects glucose metabolism. Seniors often experience changes in appetite and dietary habits too.
Hormonal changes also occur with age. These changes can affect blood sugar regulation. For instance, stress hormones may increase, leading to higher blood sugar levels.
Seniors may also take medications for other health issues. Some of these medications can interfere with blood sugar control. Therefore, it is crucial for diabetic seniors to monitor their condition closely.
Symptoms in Elderly Diabetics
Recognizing symptoms is vital for timely intervention. Common signs of diabetes include:
Increased thirst
Frequent urination
Fatigue
Blurred vision
Slow-healing wounds
These symptoms can be mistaken for normal aging signs. Awareness is key for proper diagnosis and management.
Importance of Regular Check-ups
Regular medical check-ups are essential for seniors. Doctors can monitor blood sugar levels effectively during these visits. Early detection of diabetes allows for better management strategies.
Lifestyle changes can significantly impact health outcomes. Diet modifications and increased physical activity can help manage diabetes effectively.
Types of Diabetes
Type 1 Diabetes
Type 1 diabetes occurs when the body cannot produce insulin. This type is often diagnosed in children and young adults. It is less common than type 2 diabetes. People with type 1 diabetes need to take insulin daily to manage their blood sugar levels. This chronic condition can lead to serious health issues if not treated properly.
Type 2 Diabetes
Type 2 diabetes is the most prevalent form of diabetes, especially among older adults. In fact, it accounts for about 90-95% of all diabetes cases. This type develops when the body becomes resistant to insulin or does not produce enough insulin.
Older adults are at a higher risk due to various factors like age, obesity, and physical inactivity. As people age, muscle mass decreases, and fat increases, which may contribute to insulin resistance. This can lead to higher blood sugar levels over time.
In the United States, around 25% of seniors aged 65 and older have type 2 diabetes. Many do not even realize they have it. Symptoms can be mild or go unnoticed until complications arise. Regular screenings are crucial for early detection.
Gestational Diabetes
Gestational diabetes occurs during pregnancy and typically resolves after childbirth. It happens when the body cannot produce enough insulin during pregnancy. While this condition mainly affects women who are pregnant, it is rare in elderly individuals.
However, some older women may experience similar symptoms due to other health conditions. It’s important for seniors to discuss any unusual symptoms with their healthcare provider. Knowing the signs can aid in early diagnosis and treatment.
Chronic Diabetes Conditions
Chronic diabetes conditions refer to long-term complications that arise from uncontrolled blood sugar levels. These include heart disease, kidney damage, and nerve damage. Older adults with diabetes face a higher risk of these complications.
Managing blood sugar levels through diet, exercise, and medication can help prevent these issues. Regular check-ups with healthcare providers are essential for monitoring overall health.
Common Symptoms in Older Adults
Fatigue
Fatigue is a common symptom of diabetes. Older adults often feel tired or weak. This exhaustion can result from the body not using sugar properly for energy. As a result, daily activities may become challenging.
In some cases, fatigue can also lead to mood changes. Irritability may increase as energy levels drop. Recognizing this symptom early is crucial. It allows for timely medical advice and intervention.
Increased Thirst
Increased thirst is another significant sign of diabetes. Older adults might notice they are drinking more water than usual. This happens because high blood sugar levels cause the body to lose fluids.
When the kidneys work harder to filter out excess sugar, they also lose water. This can lead to dehydration. If an elderly person feels thirsty constantly, it could indicate a problem.
Weight Loss
Unintentional weight loss can occur in older adults with diabetes. Some individuals may not understand why they are losing weight. They might eat normally but still shed pounds.
This weight loss happens because the body starts using fat and muscle for energy instead of sugar. It signals that the body struggles to manage glucose levels effectively. Recognizing this symptom early can help prevent further health issues.
Frequent Urination
Frequent urination is a common issue for elderly individuals with diabetes. The need to urinate often disrupts daily life, especially at night. This occurs because the kidneys filter out extra sugar, drawing water with it.
As a result, fluid levels drop, leading to increased thirst and more frequent trips to the bathroom. Noticing this pattern can be vital for early diagnosis.
Slow Healing Wounds
Slow healing wounds can also indicate diabetes in older adults. Cuts and sores may take longer to heal than expected. High blood sugar levels affect circulation and immune response.
This makes it harder for the body to repair itself. If an elderly person has wounds that do not heal, it is essential to seek medical advice.
Importance of Early Recognition
Recognizing these symptoms early is critical for effective management of diabetes. Early detection can lead to better treatment options. It helps prevent complications such as heart disease or nerve damage.
Family members should watch for these signs in their loved ones. Regular check-ups with healthcare providers are important as well. These actions can significantly improve quality of life for older adults dealing with diabetes.
Unique Signs in Seniors
Numbness or Tingling
Numbness or tingling in the extremities is a common sign of diabetes in older adults. This sensation often occurs in the hands and feet. It happens due to nerve damage caused by high blood sugar levels over time. Many seniors may dismiss this feeling as normal aging. However, it can indicate diabetic neuropathy, a serious condition that requires attention.
Ignoring these symptoms can lead to more severe complications. Seniors should report any unusual sensations to their healthcare provider. Early detection can help manage diabetes effectively and prevent further nerve damage.
Slower Healing Process
A slower healing process for cuts and infections is another significant sign of diabetes in seniors. High blood sugar levels can impair the body’s ability to heal wounds. This delay can be troubling, especially for elderly individuals who are more prone to injuries. A small cut might take longer than usual to heal, leading to potential infections.
Seniors with diabetes may find that even minor wounds become problematic. They should monitor any injuries closely and seek medical help if healing does not occur as expected. Proper wound care is essential for preventing serious complications.

Blurred Vision
Blurred vision can be a critical indicator of diabetes in older adults. When blood sugar levels fluctuate, they can affect the lens of the eye. This change leads to temporary vision problems. Seniors may notice difficulty focusing on objects or reading fine print.
If blurred vision persists, it could signal more severe issues like diabetic retinopathy. This condition damages the retina and can lead to blindness if untreated. Regular eye exams are crucial for seniors with diabetes. These exams help detect changes early and provide necessary interventions.
Other Factors
Several other factors can contribute to the signs of diabetes in seniors. Age plays a role in how symptoms present themselves. Older adults may experience fatigue or increased thirst but attribute these feelings to aging rather than diabetes.
Lifestyle choices also impact how diabetes manifests. Poor diet, lack of exercise, and obesity increase risks. Awareness of these factors helps seniors understand their health better.
Importance of Early Testing
Regular Screenings
Older adults should undergo regular screenings for diabetes. Many seniors may not show obvious signs. Routine testing can catch diabetes early. The American Diabetes Association recommends that adults aged 45 and older get tested every three years. Those with risk factors should be screened more often. These factors include obesity, a family history of diabetes, or high blood pressure.
Healthcare providers play a crucial role in this process. They can assess each patient’s risk and recommend appropriate tests. Blood tests are the most common method for diagnosing diabetes. A fasting blood sugar test measures glucose levels after an overnight fast. An A1C test provides an average blood sugar level over the past two to three months. Both tests help identify diabetes before serious complications arise.
Preventing Complications
Early detection of diabetes can prevent severe health problems. Uncontrolled diabetes can lead to complications like heart disease, kidney failure, and vision loss. Seniors are particularly vulnerable to these issues. Regular testing allows for timely intervention. This can include lifestyle changes, medication, or insulin therapy.
For example, a senior diagnosed early might change their diet and increase physical activity. These changes can stabilize blood sugar levels and improve overall health. Avoiding complications is essential for maintaining quality of life in older adults.
Role of Healthcare Providers
Healthcare providers are vital in managing diabetes risks among the elderly. They should educate patients about the importance of regular testing. Providers can explain the types of tests available and when they should be done. This guidance helps seniors understand their health better.
Providers also monitor patients’ progress after diagnosis. They adjust treatment plans based on individual needs and responses to therapy. This ongoing support is important for effective management of diabetes.
Managing Type 2 Diabetes
Lifestyle Changes
Lifestyle changes play a crucial role in managing diabetes. A balanced diet is essential. Foods high in fiber, such as fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, can help control blood sugar levels. Limiting sugar and refined carbs is also important. These changes can prevent complications associated with untreated diabetes.
Regular meal times can aid in maintaining steady blood glucose levels. Portion control is vital too. Eating smaller meals more frequently helps avoid spikes in blood sugar. Hydration matters as well. Drinking water instead of sugary drinks supports overall health.
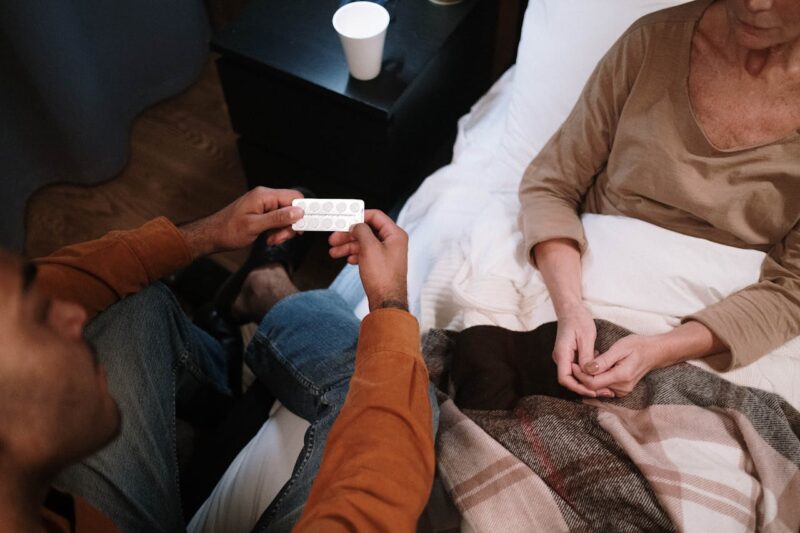
Medication Adherence
Adhering to prescribed medications is key for effective diabetes management. Medications help manage blood glucose levels and prevent complications. Missing doses can lead to elevated blood sugar and serious health risks.
Diabetes care management includes regular communication with healthcare providers. They can adjust medications based on individual needs. Patients should keep track of their medications and understand their purpose. This knowledge empowers them in their diabetes self-management journey.
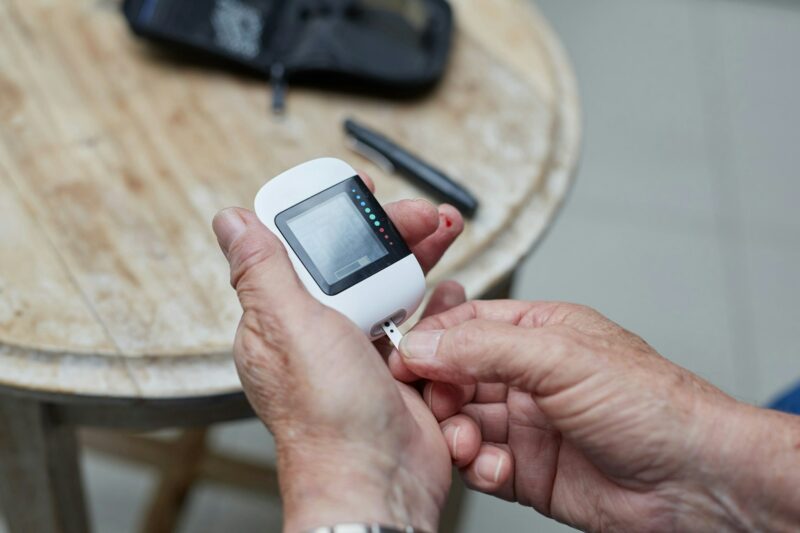
Blood Sugar Monitoring
Monitoring blood sugar levels regularly is essential for diabetics. It helps identify patterns and triggers that affect glucose levels. Keeping a log of readings provides valuable information for doctors.
Patients should learn how to use glucose meters correctly. Understanding target ranges allows for better management of diabetes symptoms. Adjustments to diet or medication may be necessary based on these readings.
Regular Physical Activity
Physical activity aids in controlling blood glucose levels. Engaging in at least 150 minutes of moderate exercise each week is recommended. Activities like walking, swimming, or cycling can improve insulin sensitivity.
Exercise also helps maintain a healthy weight. Weight management reduces the risk factors associated with the diabetes epidemic. Regular physical activity boosts energy levels and enhances overall well-being.

Balanced Nutrition
Balanced nutrition is vital in managing type 2 diabetes effectively. A diet rich in nutrients supports overall health and aids blood glucose control. Including lean proteins, healthy fats, and complex carbohydrates ensures a well-rounded diet.
Meal planning can simplify healthy eating habits. Preparing meals ahead of time helps avoid unhealthy choices when busy or stressed. Consulting a registered dietitian can provide personalized guidance for optimal nutrition.
Diabetes Management Challenges
Managing diabetes presents challenges, especially for the elderly. Cognitive decline may affect self-management skills. Support from family members or caregivers can make a significant difference.
Understanding the diabetes type confusion is also crucial. Knowing whether one has type 1 or type 2 diabetes affects treatment decisions. Proper education about the condition leads to better outcomes and improved quality of life.
Impact on Senior Health
Health Problems
Diabetes can worsen existing health problems in the elderly. Many seniors already face challenges like heart disease, arthritis, or high blood pressure. Diabetes can complicate these conditions. For instance, high blood sugar levels can lead to increased inflammation in the body. This inflammation may intensify joint pain for those with arthritis.
Diabetes affects circulation. Poor circulation can worsen heart conditions and increase the risk of heart attacks. Seniors with diabetes are also more likely to experience complications from infections. This is due to a weakened immune system caused by high blood sugar levels.
Risk Factors
Several risk factors contribute to diabetes in older adults. Age itself is a significant factor. As people age, their bodies become less efficient at processing glucose. Sedentary lifestyles also play a role. Many seniors do not engage in regular physical activity, which can lead to weight gain and increased insulin resistance.
Diet is another important aspect. Seniors may consume diets high in carbohydrates and sugars, which can raise blood sugar levels. These dietary choices can lead to obesity and other health issues. Understanding these risk factors helps in preventing diabetes or managing it effectively.
Increased Hospitalizations
Seniors with diabetes face a higher chance of increased hospitalizations due to complications. Common complications include diabetic ketoacidosis and hyperglycemic crises. These conditions require urgent medical attention. They can arise suddenly, leading to emergency room visits.
Moreover, complications such as foot ulcers or infections may develop due to poor circulation and nerve damage. These issues often require hospitalization for treatment or surgery. The need for frequent medical care can strain both patients and healthcare systems.
Emotional Effects
Managing diabetes has significant emotional and mental health effects on seniors. Many feel overwhelmed by the constant need to monitor their blood sugar levels. This responsibility can lead to feelings of anxiety or depression.
ial isolation may also occur. Seniors might avoid social gatherings if they feel embarrassed about their condition or dietary restrictions. This isolation can further impact their mental health, leading to loneliness.
Support systems are crucial for managing both the physical and emotional aspects of diabetes. Family members and friends can provide encouragement and assistance with daily tasks related to care.
When to Seek Medical Advice
Severe Symptoms
Recognizing severe symptoms of diabetes is crucial for the elderly. These symptoms can indicate a medical emergency. Signs like excessive thirst, frequent urination, and extreme fatigue should not be ignored.
Unexplained weight loss may also signal a problem. Seniors should pay attention to cuts or bruises that heal slowly. These can suggest poor blood circulation due to diabetes. If any of these symptoms appear, it is essential to seek immediate medical attention.
Regular Check-ups
Regular visits to the doctor are vital for seniors. Routine check-ups can help catch diabetes early. Doctors often conduct blood tests to monitor sugar levels. This proactive care can prevent complications later on.
Seniors should discuss any changes in their health with healthcare professionals. Even minor concerns deserve attention. Early diagnosis leads to better management of diabetes.
Consult Healthcare Professionals
Elderly individuals must consult healthcare professionals when they notice symptoms. Family members can help by encouraging them to make appointments. Sometimes, seniors may downplay their symptoms, thinking they are just part of aging.
Healthcare providers can offer guidance and support. They provide personalized care plans based on individual needs. This tailored approach helps manage diabetes effectively.
Don’t Ignore Symptoms
Ignoring symptoms attributed to aging can be dangerous. Many assume fatigue or increased thirst is just part of getting older. However, these could be early signs of diabetes.
Seniors must understand that changes in their body require attention. It is essential to communicate openly with doctors about all health issues. This includes discussing any new or worsening symptoms.
Importance of Education
Education about diabetes and its signs is key for the elderly. Understanding the condition helps them recognize when something is wrong. Family members should also educate themselves about diabetes signs.
Support from family can encourage seniors to seek help when needed. Providing information about diabetes can empower them to take charge of their health.
Final Remarks
Understanding the signs of diabetes in the elderly is crucial for you and your loved ones. Recognizing common and unique symptoms can lead to early detection and better management of the condition. This knowledge empowers you to take action, ensuring seniors receive the care they need to maintain their health and well-being.
Don’t wait for symptoms to escalate. Stay informed, schedule regular check-ups, and encourage open discussions about health with your family members. The sooner you act, the better the outcomes for everyone involved. Make diabetes awareness a priority today!
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the early signs of diabetes in the elderly?
Early signs include increased thirst, frequent urination, fatigue, and blurred vision. Recognizing these symptoms is crucial for timely intervention.
How can diabetes affect mental health in seniors?
Diabetes can lead to depression and anxiety due to stress from managing the condition. Mental health support is essential for overall well-being.
Are there specific risk factors for diabetes in older adults?
Yes, risk factors include obesity, sedentary lifestyle, family history, and previous gestational diabetes. Awareness helps in prevention and management.
How is Type 2 diabetes diagnosed in seniors?
Diagnosis typically involves blood tests like fasting glucose or HbA1c levels. Regular screenings are vital for early detection.
What lifestyle changes can help manage diabetes in seniors?
Healthy eating, regular exercise, and weight management are key. These changes improve blood sugar control and enhance overall health.
When should seniors seek medical advice regarding diabetes?
Seniors should consult a healthcare provider if they experience persistent symptoms like increased thirst or unexplained weight loss. Early intervention is crucial.
Can diabetes be reversed in older adults?
While Type 2 diabetes may not be completely reversible, it can be effectively managed through lifestyle changes and medication, improving quality of life.